目录
概述
事件起因,一哥们在群里面贴出了类似下面这样的一段代码:
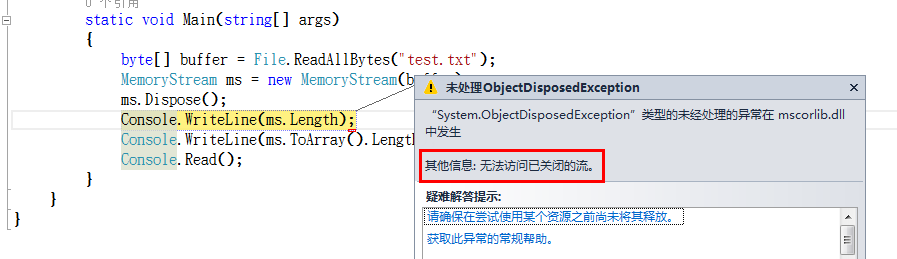
1 class Program 2 { 3 static void Main(string[] args) 4 { 5 byte[] buffer = File.ReadAllBytes("test.txt"); 6 MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream(buffer); 7 ms.Dispose(); 8 Console.WriteLine(ms.ToArray().Length); 9 Console.Read();10 }11 } 先不去考究这段代码到底有没有什么意义,就代码而言,内存流释放之后,再去使用ms会有问题么?
运行结果:
那我们如果访问ms对象的其他的属性(ms.Length)会怎么样呢?
访问其它的方法它也会出现上面的异常。
这问题出来了,难道内存流的Dispose方法是选择性的释放?
在看MemoryStream分析之前,回顾一下托管与非托管资源的概念。
托管资源
一般是指被CLR控制的内存资源,这些资源的管理可以由CLR来控制,例如程序中分配(new)的对象,作用域内的变量等。
非托管资源
是CLR不能控制或者管理的部分,这些资源有很多,比如文件流,数据库的连接,系统的窗口句柄(Window内核对象(句柄))、字体、刷子、dc打印机资源等等……这些资源一般情况下不存在于Heap(内存中用于存储对象实例的地方)中。
C#的垃圾回收器:
CLR为程序员提供的内存管理机制,使得程序员在编写代码时不需要显式的去释放自己使用的内存资源(这些在先前C和C++中是需要程序员自己去显式的释放的)。这种管理机制称为GC(garbage collection)。GC的作用是很明显的,当系统内存资源匮乏时,它就会被激发,然后自动的去释放那些没有被使用的托管资源(也就是程序员没有显式释放的对象)。对于那些非托管资源虽然垃圾回收器可以跟踪封装非托管资源的对象的生存期,但它不了解具体如何清理这些资源。还好.net提供了Finalize()方法,它允许在垃圾回收器回收该类资源时,适当的清理非托管资源。但是Finalize()会产生很多副作用。释放非托管资源
资源的释放一般是通过"垃圾回收器"自动完成的,但具体来说,仍有些需要注意的地方:
1、值类型和引用类型的引用其实是不需要什么"垃圾回收器"来释放内存的,因为当它们出了作用域后会自动释放所占内存,因为它们都保存在栈(Stack)中; 2、只有引用类型的引用所指向的对象实例才保存在堆(Heap)中,而堆因为是一个自由存储空间,所以它并没有像"栈"那样有生存期("栈"的元素弹出后就代表生存期结束,也就代表释放了内存),并且要注意的是,"垃圾回收器"只对这块区域起作用。 然而,有些情况下,当需要释放非托管资源时,就必须通过写代码的方式来解决。非托管资源的释放
当我们在类中封装了对非托管资源的操作时,我们就需要显式释放(Dispose),或隐式释放(Finalize)的释放这些资源。
Finalize一般情况下用于基类不带close方法或者不带Dispose显式方法的类,也就是说,在Finalize过程中我们需要隐式的去实现非托管资源的释放,然后系统会在Finalize过程完成后,自己的去释放托管资源。如果要实现Dispose方法,可以通过实现IDisposable接口,这样用户在使用这个类的同时就可以显示的执行Dispose方法,释放资源。(详细的内容可参考:)
MemoryStream分析
对于这个问题,吃饭的时候一直很纠结,所以就查了一些这方面的资料,也试图反编译MemoryStream类,看看Dispose方法是如何实现。
参考:
github上MemoryStream中的代码:
1 // 2 // System.IO.MemoryStream.cs 3 // 4 // Authors: Marcin Szczepanski (marcins@zipworld.com.au) 5 // Patrik Torstensson 6 // Gonzalo Paniagua Javier (gonzalo@ximian.com) 7 // Marek Safar (marek.safar@gmail.com) 8 // 9 // (c) 2001,2002 Marcin Szczepanski, Patrik Torstensson 10 // (c) 2003 Ximian, Inc. (http://www.ximian.com) 11 // Copyright (C) 2004 Novell, Inc (http://www.novell.com) 12 // Copyright 2011 Xamarin, Inc (http://www.xamarin.com) 13 // 14 // Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining 15 // a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the 16 // "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including 17 // without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, 18 // distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to 19 // permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to 20 // the following conditions: 21 // 22 // The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be 23 // included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software. 24 // 25 // THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, 26 // EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF 27 // MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND 28 // NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE 29 // LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION 30 // OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION 31 // WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE. 32 // 33 34 using System.Globalization; 35 using System.Runtime.InteropServices; 36 using System.Threading; 37 #if NET_4_5 38 using System.Threading.Tasks; 39 #endif 40 41 namespace System.IO 42 { 43 [Serializable] 44 [ComVisible (true)] 45 [MonoLimitation ("Serialization format not compatible with .NET")] 46 public class MemoryStream : Stream 47 { 48 bool canWrite; 49 bool allowGetBuffer; 50 int capacity; 51 int length; 52 byte [] internalBuffer; 53 int initialIndex; 54 bool expandable; 55 bool streamClosed; 56 int position; 57 int dirty_bytes; 58 #if NET_4_5 59 [NonSerialized] 60 Task read_task; 61 #endif 62 63 public MemoryStream () : this (0) 64 { 65 } 66 67 public MemoryStream (int capacity) 68 { 69 if (capacity < 0) 70 throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ("capacity"); 71 72 canWrite = true; 73 74 this.capacity = capacity; 75 internalBuffer = new byte [capacity]; 76 77 expandable = true; 78 allowGetBuffer = true; 79 } 80 81 public MemoryStream (byte [] buffer) 82 { 83 if (buffer == null) 84 throw new ArgumentNullException ("buffer"); 85 86 InternalConstructor (buffer, 0, buffer.Length, true, false); 87 } 88 89 public MemoryStream (byte [] buffer, bool writable) 90 { 91 if (buffer == null) 92 throw new ArgumentNullException ("buffer"); 93 94 InternalConstructor (buffer, 0, buffer.Length, writable, false); 95 } 96 97 public MemoryStream (byte [] buffer, int index, int count) 98 { 99 InternalConstructor (buffer, index, count, true, false);100 }101 102 public MemoryStream (byte [] buffer, int index, int count, bool writable)103 {104 InternalConstructor (buffer, index, count, writable, false);105 }106 107 public MemoryStream (byte [] buffer, int index, int count, bool writable, bool publiclyVisible)108 {109 InternalConstructor (buffer, index, count, writable, publiclyVisible);110 }111 112 void InternalConstructor (byte [] buffer, int index, int count, bool writable, bool publicallyVisible)113 {114 if (buffer == null)115 throw new ArgumentNullException ("buffer");116 117 if (index < 0 || count < 0)118 throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ("index or count is less than 0.");119 120 if (buffer.Length - index < count)121 throw new ArgumentException ("index+count", 122 "The size of the buffer is less than index + count.");123 124 canWrite = writable;125 126 internalBuffer = buffer;127 capacity = count + index;128 length = capacity;129 position = index;130 initialIndex = index;131 132 allowGetBuffer = publicallyVisible;133 expandable = false; 134 }135 136 void CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ()137 {138 if (streamClosed)139 throw new ObjectDisposedException ("MemoryStream");140 }141 142 public override bool CanRead {143 get { return !streamClosed; }144 }145 146 public override bool CanSeek {147 get { return !streamClosed; }148 }149 150 public override bool CanWrite {151 get { return (!streamClosed && canWrite); }152 }153 154 public virtual int Capacity {155 get {156 CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();157 return capacity - initialIndex;158 }159 160 set {161 CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();162 163 if (!expandable)164 throw new NotSupportedException ("Cannot expand this MemoryStream");165 166 if (value < 0 || value < length)167 throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ("value",168 "New capacity cannot be negative or less than the current capacity " + value + " " + capacity);169 170 if (internalBuffer != null && value == internalBuffer.Length)171 return;172 173 byte [] newBuffer = null;174 if (value != 0) {175 newBuffer = new byte [value];176 if (internalBuffer != null)177 Buffer.BlockCopy (internalBuffer, 0, newBuffer, 0, length);178 }179 180 dirty_bytes = 0; // discard any dirty area beyond previous length181 internalBuffer = newBuffer; // It's null when capacity is set to 0182 capacity = value;183 }184 }185 186 public override long Length {187 get {188 // LAMESPEC: The spec says to throw an IOException if the189 // stream is closed and an ObjectDisposedException if190 // "methods were called after the stream was closed". What191 // is the difference?192 193 CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();194 195 // This is ok for MemoryStreamTest.ConstructorFive196 return length - initialIndex;197 }198 }199 200 public override long Position {201 get {202 CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();203 return position - initialIndex;204 }205 206 set {207 CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();208 if (value < 0)209 throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ("value",210 "Position cannot be negative" );211 212 if (value > Int32.MaxValue)213 throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ("value",214 "Position must be non-negative and less than 2^31 - 1 - origin");215 216 position = initialIndex + (int) value;217 }218 }219 220 protected override void Dispose (bool disposing)221 {222 streamClosed = true;223 expandable = false;224 }225 226 public override void Flush ()227 {228 // Do nothing229 }230 231 public virtual byte [] GetBuffer ()232 {233 if (!allowGetBuffer)234 throw new UnauthorizedAccessException ();235 236 return internalBuffer;237 }238 239 public override int Read ([In,Out] byte [] buffer, int offset, int count)240 {241 if (buffer == null)242 throw new ArgumentNullException ("buffer");243 244 if (offset < 0 || count < 0)245 throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ("offset or count less than zero.");246 247 if (buffer.Length - offset < count )248 throw new ArgumentException ("offset+count",249 "The size of the buffer is less than offset + count.");250 251 CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();252 253 if (position >= length || count == 0)254 return 0;255 256 if (position > length - count)257 count = length - position;258 259 Buffer.BlockCopy (internalBuffer, position, buffer, offset, count);260 position += count;261 return count;262 }263 264 public override int ReadByte ()265 {266 CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();267 if (position >= length)268 return -1;269 270 return internalBuffer [position++];271 }272 273 public override long Seek (long offset, SeekOrigin loc)274 {275 CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();276 277 // It's funny that they don't throw this exception for < Int32.MinValue278 if (offset > (long) Int32.MaxValue)279 throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ("Offset out of range. " + offset);280 281 int refPoint;282 switch (loc) {283 case SeekOrigin.Begin:284 if (offset < 0)285 throw new IOException ("Attempted to seek before start of MemoryStream.");286 refPoint = initialIndex;287 break;288 case SeekOrigin.Current:289 refPoint = position;290 break;291 case SeekOrigin.End:292 refPoint = length;293 break;294 default:295 throw new ArgumentException ("loc", "Invalid SeekOrigin");296 }297 298 // LAMESPEC: My goodness, how may LAMESPECs are there in this299 // class! :) In the spec for the Position property it's stated300 // "The position must not be more than one byte beyond the end of the stream."301 // In the spec for seek it says "Seeking to any location beyond the length of the 302 // stream is supported." That's a contradiction i'd say.303 // I guess seek can go anywhere but if you use position it may get moved back.304 305 refPoint += (int) offset;306 if (refPoint < initialIndex)307 throw new IOException ("Attempted to seek before start of MemoryStream.");308 309 position = refPoint;310 return position;311 }312 313 int CalculateNewCapacity (int minimum)314 {315 if (minimum < 256)316 minimum = 256; // See GetBufferTwo test317 318 if (minimum < capacity * 2)319 minimum = capacity * 2;320 321 return minimum;322 }323 324 void Expand (int newSize)325 {326 // We don't need to take into account the dirty bytes when incrementing the327 // Capacity, as changing it will only preserve the valid clear region.328 if (newSize > capacity)329 Capacity = CalculateNewCapacity (newSize);330 else if (dirty_bytes > 0) {331 Array.Clear (internalBuffer, length, dirty_bytes);332 dirty_bytes = 0;333 }334 }335 336 public override void SetLength (long value)337 {338 if (!expandable && value > capacity)339 throw new NotSupportedException ("Expanding this MemoryStream is not supported");340 341 CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();342 343 if (!canWrite) {344 throw new NotSupportedException (Locale.GetText 345 ("Cannot write to this MemoryStream"));346 }347 348 // LAMESPEC: AGAIN! It says to throw this exception if value is349 // greater than "the maximum length of the MemoryStream". I haven't350 // seen anywhere mention what the maximum length of a MemoryStream is and351 // since we're this far this memory stream is expandable.352 if (value < 0 || (value + initialIndex) > (long) Int32.MaxValue)353 throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ();354 355 int newSize = (int) value + initialIndex;356 357 if (newSize > length)358 Expand (newSize);359 else if (newSize < length) // Postpone the call to Array.Clear till expand time360 dirty_bytes += length - newSize;361 362 length = newSize;363 if (position > length)364 position = length;365 }366 367 public virtual byte [] ToArray ()368 {369 int l = length - initialIndex;370 byte[] outBuffer = new byte [l];371 372 if (internalBuffer != null)373 Buffer.BlockCopy (internalBuffer, initialIndex, outBuffer, 0, l);374 return outBuffer; 375 }376 377 public override void Write (byte [] buffer, int offset, int count)378 {379 if (buffer == null)380 throw new ArgumentNullException ("buffer");381 382 if (offset < 0 || count < 0)383 throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException ();384 385 if (buffer.Length - offset < count)386 throw new ArgumentException ("offset+count",387 "The size of the buffer is less than offset + count.");388 389 CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();390 391 if (!CanWrite)392 throw new NotSupportedException ("Cannot write to this stream.");393 394 // reordered to avoid possible integer overflow395 if (position > length - count)396 Expand (position + count);397 398 Buffer.BlockCopy (buffer, offset, internalBuffer, position, count);399 position += count;400 if (position >= length)401 length = position;402 }403 404 public override void WriteByte (byte value)405 {406 CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();407 if (!canWrite)408 throw new NotSupportedException ("Cannot write to this stream.");409 410 if (position >= length) {411 Expand (position + 1);412 length = position + 1;413 }414 415 internalBuffer [position++] = value;416 }417 418 public virtual void WriteTo (Stream stream)419 {420 CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();421 422 if (stream == null)423 throw new ArgumentNullException ("stream");424 425 stream.Write (internalBuffer, initialIndex, length - initialIndex);426 }427 428 #if NET_4_5429 430 public override Task CopyToAsync (Stream destination, int bufferSize, CancellationToken cancellationToken)431 {432 // TODO: Specialization but what for?433 return base.CopyToAsync (destination, bufferSize, cancellationToken);434 }435 436 public override Task FlushAsync (CancellationToken cancellationToken)437 {438 if (cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested)439 return TaskConstants.Canceled;440 441 try {442 Flush ();443 return TaskConstants.Finished;444 } catch (Exception ex) {445 return Task 通过上面的代码,你可以看出,很多方法和属性中都会有这样的一个方法的调用:
CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ();
该方法的实现
1 void CheckIfClosedThrowDisposed ()2 {3 if (streamClosed)4 throw new ObjectDisposedException ("MemoryStream");5 } 通过方法名可以清楚的知道该方法的作用:检查如果关闭了则抛出Dispose异常,通过方法体也可以清楚的知道该方法的作用。
你可以看一下ToArray方法1 public virtual byte [] ToArray ()2 {3 int l = length - initialIndex;4 byte[] outBuffer = new byte [l];5 6 if (internalBuffer != null)7 Buffer.BlockCopy (internalBuffer, initialIndex, outBuffer, 0, l);8 return outBuffer; 9 } 从代码中,也可以看出该方法并没有对流是否关闭进行检查。
总结
虽然上面的代码能说明为什么出现异常的原因,但是为什么要这样设计?为什么其他的方法会检测是否释放而ToArray方法反而放过呢?
功底有限,也只能到这地步,如果哪个园友有更深入的解释,可以给个合理的解释,为什么这样设计?
选择性的释放,那会不会就不安全了呢?